Breeding fish is a rewarding aspect of the aquarium hobby that requires the right environment to ensure success. Typically, a breeding tank is set up separately from the main aquarium to provide a controlled environment. Features often include adjustable water flow, temperature regulation, and appropriate substrates or plants to simulate natural breeding conditions.
Ensuring optimal water quality and providing a diet rich in nutrients are crucial for the health of both the adult fish and the offspring. Seasoned breeders sometimes use dividers or separate chambers to protect fry after birth. Fish enthusiasts invest in fish breeding tanks not only to experience the natural cycle of aquatic life but also to potentially cultivate rare or valuable species, driving the continued fascination with aquatic breeding.

Picture Credit: www.mdpi.com
Dive Into Aquaculture
The Role Of Fish Breeding Tanks
Fish breeding tanks, often called hatcheries, provide a controlled environment for the safe spawning, hatching, and early life stages of fish. These tanks support selective breeding practices. This enhances traits such as growth rates, disease resistance, and overall health. Proper tank conditions ensure high survival rates for fish fry. It also prepares them for life in larger farm systems or natural bodies of water.- Controlled water quality: Optimal pH, temperature, and cleanliness.
- Safe breeding spaces: Structures for egg laying and fry development.
- Monitoring systems: Constant checks on fish health and water conditions.
Different Scales Of Fish Farming
Fish farming encompasses diverse operations across various scales. It ranges from small-scale indoor systems to expansive outdoor aquaculture farms.| Type | Scale | Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Micron Farms | Small | Indoor/Backyard |
| Medium Enterprises | Medium | Indoor/Outdoor |
| Industrial Hatcheries | Large | Outdoor |
- Home Tanks: Ideal for hobbyists or rare species.
- Community Farms: Supports local economies and food security.
- Commercial Hatcheries: Drives global fish production.
Optimal Tank Types
Choosing The Right Material
Different materials bring unique benefits to fish breeding tanks.- Glass: It’s clear and sturdy, which means great visibility and lasting use. But it can be heavy and may crack easily if hit.
- Acrylic: This lighter option also offers clarity but is more prone to scratches. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to move.
- Plastic: Often the most affordable, plastic tanks are very lightweight. They may, however, be less durable and more opaque over time.
Pros And Cons Of Various Tank Shapes
Different tank shapes affect fish breeding in numerous ways.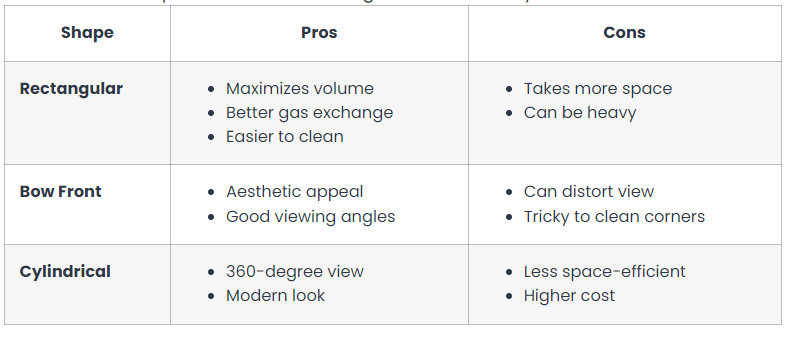
Water Quality Management
Importance Of Filtration
Filters remove waste and keep water clean. A breeding tank requires efficient filtration. Not only does it remove debris, but it also provides essential aeration and circulation.- Mechanical filters – these trap solids, clearing the water.
- Biological filters – these harbor bacteria that break down toxins.
- Chemical filters – these often use activated carbon to remove impurities.
Temperature And Ph Balance
Stable temperature and pH are critical for fish breeding. These affect your fish’s health and reproduction.| Parameter | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 76-80°F (24-27°C) |
| pH Level | 6.5-7.5 |
Breeding Tank Technics
Creating An Ideal Environment
To kick-start the breeding process, it’s crucial to mimic the natural habitat of your fish. A serene atmosphere promotes excellent breeding conditions. Here’s how to create one:- Water quality: Maintain pristine water with proper filtration and frequent changes.
- Temperature: Use a reliable heater to keep consistent water temperature.
- Lighting: Imitate natural light cycles with controlled aquarium lighting.
- Plants and decor: Include live plants and hiding spots to simulate a natural setting.
- Peaceful companions: Choose tank mates that won’t stress breeding pairs.
Common Breeding Setups And Strategies
Seasoned breeders often use specific setups tailored to their fish species. Here are some popular strategies:| Setup Type | Description | Suitable for Species |
|---|---|---|
| Separate Breeding Tank | Isolates breeding pairs for focused care. | Bettas, Cichlids |
| Community Breeding | Allows natural interactions in larger tanks. | Guppies, Mollies |
| Spawn Mops or Substrates | Encourages egg laying and hides fry. | Tetras, Barbs |
Fish Diet And Nutrition
Feeding Schedules For Different Species
Fish species have varying dietary requirements. It is critical to understand the specific needs of your fish. This knowledge guides you in establishing a feeding schedule that promotes optimal health and breeding conditions. Below is a simple breakdown for a range of common species:- Livebearers (Guppies, Mollies): Feed small amounts, 2-3 times daily.
- Cichlids: Offer food 1-2 times daily, depending on the species.
- Goldfish: Typically requires feeding 2 times per day.
- Discus: Prefer several small feedings throughout the day.
Supplements For Broodstock
Broodstock fish require additional nutrients to ensure they are in prime condition for breeding. Providing the right supplements can boost their reproductive capabilities.| Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| High-quality Proteins | Builds reproductive tissues. |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Improves overall health and vitality. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Enhances egg quality and hatch rates. |

Health And Disease Control
Routine Health Checks
Regular monitoring keeps fish in top shape. Here’s what to do:- Observe behavior: Look for changes in swimming patterns.
- Check appearance: Spot signs of physical distress.
- Test water quality: Maintain suitable pH levels and temperatures.
- Isolate new fish: Prevent diseases from entering your tank.
Common Diseases And Treatments
Disease strikes fast in tanks. Learn common ailments and solutions.| Disease | Symptoms | Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Ick | White spots, flashing | Raise temperature, medicated baths |
| Fungal infections | Cotton-like growths | Antifungal medication |
| Fin rot | Tattered fins, redness | Antibiotics, clean water |
| Velvet disease | Dusty appearance | Copper-based treatments |
Aeration And Oxygenation
Essential Aeration Systems
Effective aeration systems circulate water and add life-giving oxygen. These systems come in various forms, each with its unique benefits:- Air stones: Release fine bubbles, improving oxygen diffusion.
- Sponge filters: Double as a filtration system, trapping debris while oxygenating.
- Water pumps: Create flow, enhancing gas exchange on the water surface.
Maintaining Optimal Oxygen Levels
Maintaining the right oxygen levels is crucial for embryo and fry development. Here are steps to keep these levels optimal:- Monitor water parameters: Regular checks prevent oxygen dips.
- Clean tanks routinely: Reduces organic waste that consumes oxygen.
- Control tank population: Overcrowding leads to oxygen depletion.
Automation In Fish Breeding
Technological Advancements
The fish breeding landscape has drastically changed with tech innovations. Gone are days of manual monitoring. State-of-the-art sensors now track water conditions. Automatic feeders ensure timely nutrition. Even egg sorting has become a job for machines.- Environmental Control Systems – Perfect breeding conditions every time.
- Smart Lighting – Mimics natural light cycles to encourage spawning.
- Data Analytics Tools – Gathers insights for better breeding outcomes.
Benefits Of Automated Systems
Embracing automation brings a sea of advantages to fish breeding tanks. Fish benefit from consistent care. Breeders see healthier spawns. Time and effort reduce greatly.| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency | Machines handle routine tasks swiftly, no breaks needed. |
| Enhanced Precision | Accurate control over breeding variables like temperature and pH. |
| Improved Survival Rates | Consistent conditions lead to more fish making it to adulthood. |
| Data-Driven Decisions | Analytics support informed tweaks to breeding programs. |
Legal And Ethical Considerations
Understanding Regulations
Knowing the rules that govern fish breeding is essential. These laws help preserve local ecosystems and protect against over-breeding. Depending on where you live, regulations may vary. It’s important to research and understand these guidelines:- Permits: Some regions require permits for breeding certain types of fish.
- Species restrictions: Certain fish may be endangered or invasive, and breeding them could be illegal.
- Export and import laws: If you plan to ship fish across borders, you need to know the specific requirements.
Ethical Breeding Practices
Adhering to ethical standards is as important as following the law. Breeding fish responsibly means considering the physical and emotional well-being of the fish. Keep the following practices in mind:- Proper Tank Conditions: Ensure that your fish breeding tanks mirror a natural habitat and offer ample space for fish to thrive.
- Health Checks: Regularly monitor the health of both parent and offspring to prevent illnesses and genetic defects.
- Careful Mating Selection: Avoid inbreeding and select mates that promote strong, healthy genetics.
| Practice | Reason |
|---|---|
| Proper Habitat | Mimics natural living conditions, promotes well-being |
| Genetic Diversity | Prevents defects, encourages healthy progeny |
| Humane Treatment | Ensures ethical care of all fish |
Success Stories
Case Studies
Bold innovations deserve spotlight. Let’s explore case studies that illuminate the path to breeding excellence: First Case StudyJohn’s Neon Tetra breeding tank started with just ten pairs. With optimal water conditions and live food, he achieved 90% fry survival! Second Case StudyEmma turned her passion into profit with Angelfish. Her breeding pairs now produce over 2000 juveniles each month! Table format
Lessons From Seasoned Aquaculturists
Glean wisdom from those who’ve navigated these waters before:- Consistent Water Quality – Key to fish health and breeding.
- Proper Nutrition – Tailored diets ensure robust offspring.
- Isolation of Fry – Vital for safeguarding the young.
- Patient Observation – Spot issues early to act fast.
- Prepare breeding tanks with meticulous care.
- Choose the right species for your skill level.
- Keep detailed records of breeding cycles.

Frequently Asked Questions Of Fish Breeding Tank
How Do You Breed Fish In An Aquarium?
To breed fish in an aquarium, choose a compatible pair and provide optimal water conditions. Set up a breeding tank with hiding spots for fry. Feed the pair high-quality foods, and after spawning, remove adults to prevent them from eating the eggs or fry.
What Size Tank For Breeding Fish?
The ideal tank size for breeding fish varies; small species may need at least a 10-gallon tank, while larger fish typically require 20 gallons or more. Always research specific needs for the fish species you plan to breed.
Can Fish Reproduce In A Fish Breeding Tank?
Yes, many fish can reproduce in a fish tank if provided with the right conditions, such as appropriate water parameters and a conducive environment for breeding.
What’s The Easiest Fish To Breed?
The easiest fish to breed in captivity is the guppy due to its high fertility and simple tank requirements.
Conclusion
Caring for your aquatic family is a rewarding venture, and a well-planned fish breeding tank is key. Success hinges on attention to tank conditions, diet, and stress-free environments. Embrace these best practices, and you’ll likely see your finned friends flourish.
Dive into fish breeding confidently—your aquarium awaits its new, lively additions.









